AP-MS to Study FOSL Related Proteins Interactome
Proteins represent the key interacting biomolecules in the complex network within the cell and their interactions are crucial in orchestrating all aspects of life at the molecular level. Most biochemical functions are not carried out by a specific protein in isolation but by the multiple protein in associations refereed as a protein-protein interactions (PPIs).
Affinity purification-based mass spectrometry (AP-MS) is a technique of choice in discovering PPIs. These experiments are usually carried out by coupling a bait protein to the protein A or immunoglobulin G (IgG) surfaces or an affinity matrix followed by purification of tagged protein from a cell lysate. Additionally, suitable negative control replicates are mandatorily included to define the non-specific background. The composition of PPIs are then delineated by mass spectrometry analysis. These types of studies are useful in understanding the complicated interplay of proteins inside the cells for generating new hypothesis or may be helpful in placing a specific interactor in a pathway to explain observed phenotypes.
We used AP-MS method to study interactome of FOS related proteins (FOSL1 and FOSL2) in human Th17 cells. The fate of Th17 cells is regulated by various transcription factors such as BATF, IRF4 and STAT3. Furthermore, the members of the activator protein (AP-1) family including ATF, FOS and JUN also modulate the differentiation of Th17 cells. Of these AP-1 members, FOS related proteins regulates variety of processes such as cancer progression, embryonic development and immune cells signaling. In order to understand how FOS related proteins mediates signaling mechanism in Th17 cells, we performed their interactome analysis.
The analysis resulted in the identification of 163 and 67 proteins for FOSL1 and FOSL2 respectively. These interactors have passed certain criteria including mass spectrometry interaction statistics (MiST) algorithm scores with the matching IgG controls and they were mapped against in house common contaminant detected in related AP-MS experiments.
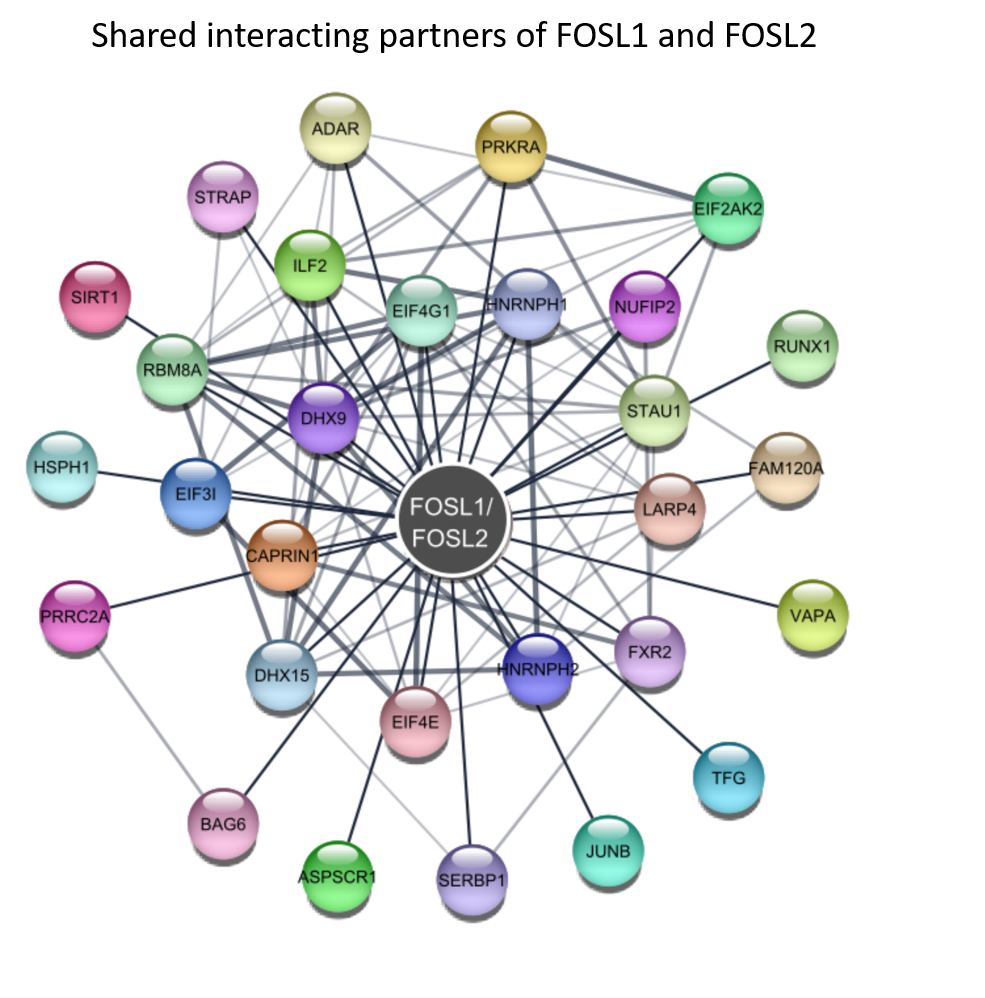
Furthermore, we validated the interesting binding partners of FOSL1 and FOSL2 by western blotting and parallel reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. The shared interactors between FOSL1 and FOSL2 as depicted in below figure were mapped against the STRING database to construct a network using Cytoscape.
The gene ontology based molecular functional analysis were performed by ClueGO and CluePedia apps built in Cytoscape.